Financial Stability Review 2020 II
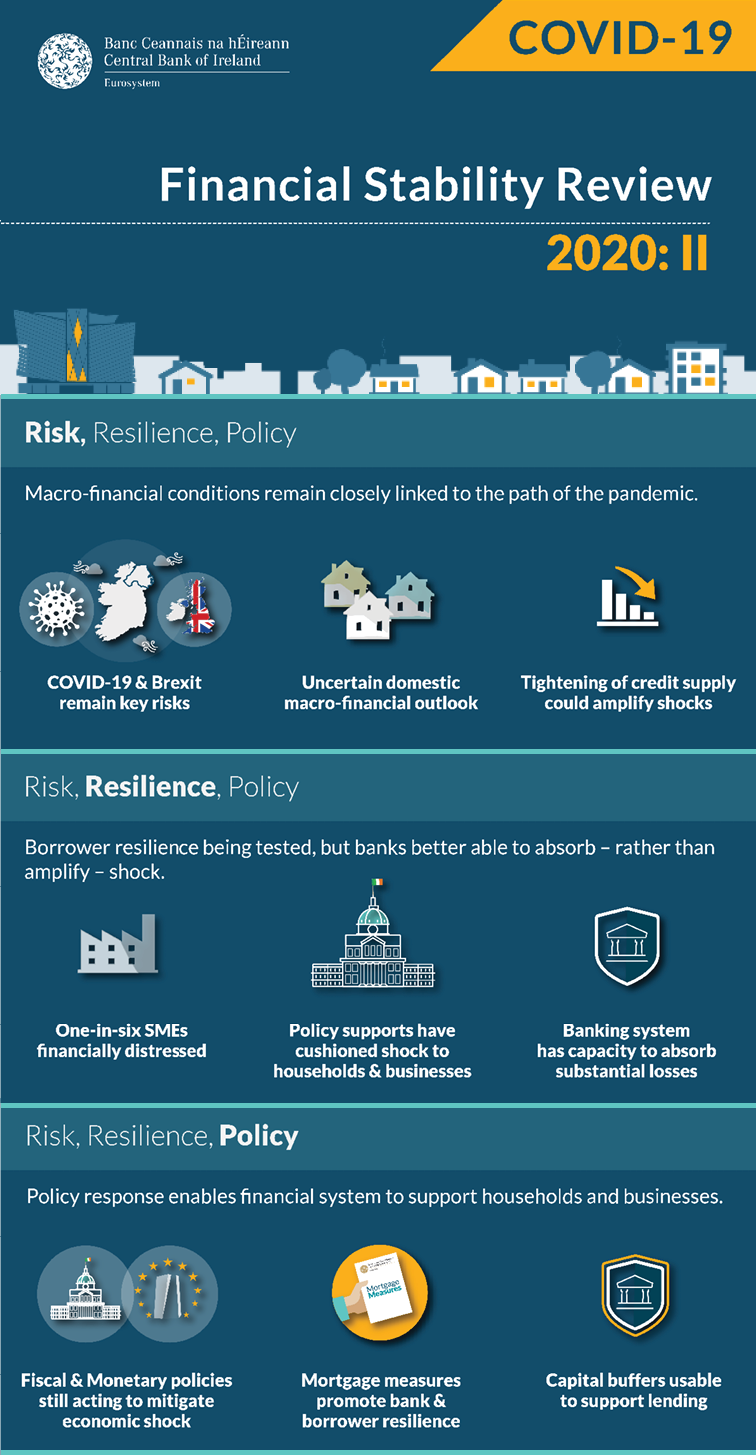
The measures taken to protect public health in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have triggered an extraordinary economic shock. While the global and domestic economies have started to recover from the depths of the crisis, the second wave of the virus poses additional near term challenges. Notwithstanding progress around the development of an effective vaccine, the main risks stem from the possibility of further pandemic-related disruption to domestic and global economic activity; the related risk of further financial market stresses; and the adverse macroeconomic implications of trading arrangements at the end of the Brexit transition period. The full transmission of the shock to the economy and financial system will take time.
The Central Bank has assessed the impact of different scenarios on the forward-looking financial position of the retail banking system. The loss-absorbing capacity of the system as a whole is sufficient to absorb shocks that are materially worse than current baseline projections. However, that loss-absorbing capacity is not without limits, and lenders should prepare for a wide variety of potential outcomes. The Central Bank’s analysis also illustrates that the macroeconomic downturn would be worse if the banking system were to restrict the supply of credit materially. To mitigate against this risk, policymakers have responded with a range of fiscal, monetary, macroprudential and microprudential actions.
Financial Stability Review 2020: II | pdf 1968 KB
 FSR 2020 II - Risk Chartpack | xls 5894 KB
FSR 2020 II - Resilience Chartpack | xls 532 KB
FSR 2020 II - Policy Chartpack | xls 396 KB
FSR 2020 II - Box Chartpack | xls 273 KB
FSR 2020 II - Risk Chartpack | xls 5894 KB
FSR 2020 II - Resilience Chartpack | xls 532 KB
FSR 2020 II - Policy Chartpack | xls 396 KB
FSR 2020 II - Box Chartpack | xls 273 KB
See also: